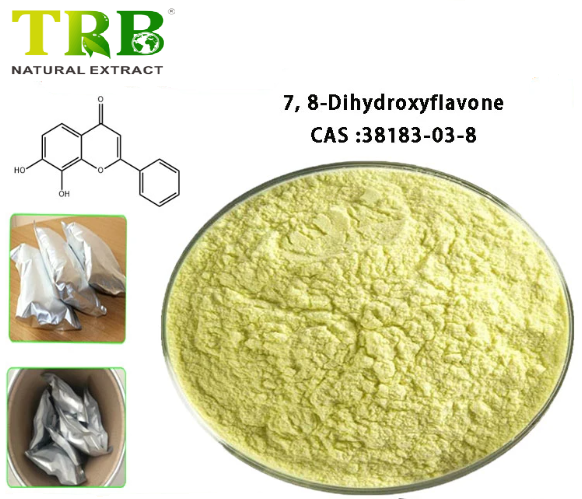
Product Name:7,8-Dihydroxyflavone
CAS No:38183-03-87
Other Name:7,8-DIHYDROXYFLAVONE;7,8-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4-benzopyrone;
DIHYDROXYFLAVONE, 7,8-(RG);7,8-Dihydroxyflavone hydrate;
7,8-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-1-benzopyran-4-one,,8-Dihydroxyflavone (7,8-DHF)
Specifications: 98.0%
Colour: Yellow powder with characteristic odor and taste
GMO Status:GMO Free
Packing: in 25kgs fiber drums
Storage:Keep container unopened in cool, dry place,Keep away from strong light
Shelf Life:24 months from date of production
Product Description: 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone (7,8-DHF) – A Multifaceted Compound for Neuroprotection and Cognitive Enhancement
Overview
7,8-Dihydroxyflavone (7,8-DHF), a naturally occurring flavonoid found in plants such as Tridax procumbens and Godmania aesculifolia, is a versatile bioactive compound with dual mechanisms of action. It acts as a selective TrkB receptor agonist (mimicking brain-derived neurotrophic factor, BDNF) and a competitive inhibitor of pyridoxal phosphatase (PDXP). These properties make it a promising candidate for neurological research, cognitive enhancement, and therapeutic applications.
Key Features
- Molecular Profile
- Chemical Formula: C₁₅H₁₀O₄
- CAS Number: 38183-03-8
- Molecular Weight: 254.24 g/mol
- Purity: ≥98% (HPLC verified)
- Solubility:
- Highly soluble in DMSO (up to 100 mM) and ethanol (25 mM)
- Sparingly soluble in water (<1 mg/mL).
- Storage & Handling
- Powder: Store at -20°C in a desiccated environment (stable for 3 years).
- Solutions: Aliquot and store at -80°C (stable for 1–2 years).
- Safety Precautions:
- Use protective gloves, goggles, and lab coats.
- Avoid inhalation, ingestion, or direct skin contact.
- Follow GHS hazard classifications (acute toxicity, eye/skin irritation).
Mechanisms of Action
- TrkB Receptor Agonism
- Binds to TrkB with high affinity (Kd ≈ 320 nM), activating downstream pathways (PI3K/Akt, MAPK) to promote:
- Neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity.
- Neuroprotection against oxidative stress, excitotoxicity, and apoptosis.
- Cognitive enhancement in models of Alzheimer’s disease, traumatic brain injury, and depression.
- PDXP Inhibition
- Competitively inhibits pyridoxal phosphatase (PDXP), increasing pyridoxal 5’-phosphate (PLP), the active form of vitamin B5.
- Benefits:
- Reverses age-dependent PLP decline in the hippocampus.
- Improves learning and memory in preclinical models.
- Additional Effects
- Antioxidant Activity: Suppresses JNK/NF-κB pathways to reduce inflammation.
- Metabolic Regulation: Enhances glucose uptake and lowers blood glucose levels.
Applications
- Neurological Research
- Study neuroprotection in Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and ischemic stroke models.
- Investigate BDNF/TrkB signaling in synaptic plasticity and mood disorders.
- Cognitive Health Supplements
- Potential use in nootropics for memory enhancement and neuroplasticity.
- Therapeutic Development
- Explore dual-target strategies (TrkB + PDXP) for vitamin B6 deficiency-related cognitive decline.
Safety & Dosage
- Toxicity: Preclinical studies show no significant toxicity at therapeutic doses.
- Recommended Dosage (research use only):
- In vitro: 250 nM–10 µM.
- In vivo (mice): 50–100 mg/kg/day orally or via intraperitoneal injection.
Why Choose 7,8-DHF?
- Dual-Action Profile: Combines TrkB activation and PDXP inhibition for multifaceted benefits.
- Blood-Brain Barrier Penetration: Effective in central nervous system targeting.
- Research-Backed: Validated in over 50 preclinical studies for neuroprotection, cognitive enhancement, and metabolic regulation.
Keywords: TrkB agonist, PDXP inhibitor, neuroprotective agent, cognitive enhancer, flavonoid benefits, 7,8-DHF solubility, Alzheimer’s research, BDNF mimic.