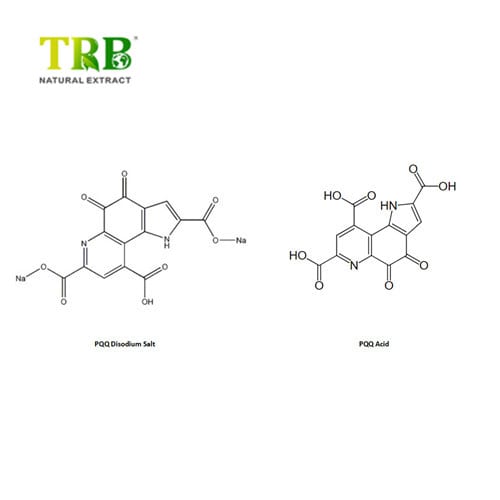
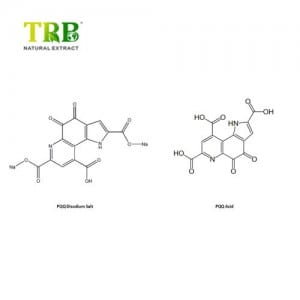
Product Name:Pyrroloquinoline Quinone Disodium Salt
CAS number: 122628-50-6/ 72909-34-3
Molecular Weight: 374.17/ 330.21
Molecular Formula: C14H4N2Na2O8/ C14H6N2O8
Specification:PQQ Disodium Salt 99%;PQQ Acid 99%
Appearance: Reddish orange to Reddish Brown Fine Powder.
Application: Widely used for dietary supplement and nutraceuticals.
Storage: Stored in a relaxed and dry condition, get away from direct sun.
Pyrroloquinoline Quinone food sources
PQQ naturally exists in most vegetable foods, fruits, and vegetables (trace), and relatively high levels of PQQ can be detected in fermented soybean products, such as kiwifruit, lychee, green beans, tofu, rapeseed, mustard, green tea (camellia), green pepper, spinach, etc.
G. Haug found that it was the third redox cofactor in bacteria after nicotinamide and flavin (although he assumed it was naphthoquinone). Anthony and Zatman also found unknown redox cofactors in ethanol dehydrogenase. In 1979, Salisbury and his colleagues as well as Duine and their colleagues extracted this pseudo base from methanol dehydrogenase of dinoflagellates and identified its molecular structure. Adachi and his colleagues found that Acetobacter also contains PQQ.
Mechanism of action of Pyrroloquinoline Quinone
Pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) is a small quinone molecule, which has a redox effect, can reduce oxidant (antioxidant); it then is recovered into the active form by glutathione. It seems relatively stable because it can undergo thousands of cycles before depletion, and it is new because it is related to the protein structure of cells (some antioxidants, main carotenoids such as beta-carotene and astaxanthin, are located in specific areas of cells, where they play more antioxidant roles proportionally). Because of proximity, PQQ seems to play a role near proteins such as carotenoids on cell membranes.
These redox functions can alter protein functions and signal transduction pathways. Although there are many promising studies in vitro (outside living models), some promising results of PQQ supplementation are mainly related to altering some signal transduction pathways or their benefits to mitochondria. (Produce more and improve efficiency).
It’s a coenzyme in bacteria (so for bacteria, it’s like B-vitamins), but it doesn’t seem to extend to humans. Since this does not apply to humans, a 2003 article in Nature, a scientific journal, argues that the idea that PQ is a vitamin compound is outdated and at best considered as a “vitamin-like substance.”
Perhaps most notable is the effect of PQQ on mitochondria, which provide energy (ATP) and regulate cell metabolism. Researchers have extensively observed the impact of PPQ on mitochondria and found that PQQ can increase the number of mitochondria and even improve the efficiency of mitochondria. This is an important reason why PPQ is so useful. Enzymes containing PQQ are known as glucose dehydrogenase, a quinoa protein that is used as a glucose sensor.
Benefits of Pyrroloquinoline Quinone
Having the mitochondria at their best is so essential for a healthy life that you can experience many benefits while taking ppq. Here are some of the most noteworthy about pyrroloquinoline quinone benefits.
Increasing Cell Energy
Because mitochondria generate energy for cells, and PQQ helps mitochondria work more effectively, energy in cells increases as a whole; this is the Pyrroloquinoline Quinone mitochondrial mechanism. Unused cellular energy is diverted to other parts of the body. If your body lacks power all day, or you feel tired or drowsy, then the increased strength of PPQ is vital to you. One study found that after taking PQQ, subjects with reported energy problems had significantly lower levels of fatigue. If you are looking for something to increase your energy, PQQ may help with that.
Preventing cognitive decline
With the development of science, scientists have found that nerve growth factor (NGF) can grow and recover. At the same time, PQQ has been shown to have a positive effect on NGF and to increase nerve growth by 40 times. NGF is essential for the formation and maintenance of new neurons, and it can restore damaged neurons that may inhibit cognitive function. Neurons are cells that transmit information, so our brains can communicate between themselves and other parts of the body. Improving the quality and quantity of neurons can improve cognition. Therefore, PQQ has short-term improvement.
Supporting cardiovascular health
Pyrroloquinoline quinine provides antioxidant and mitochondrial support. Studies have shown that both PQQ and CoQ10 support myocardial function and proper cellular oxygen utilization. Pyrroloquinoline quinone prevents oxidative stress through its rejuvenation.
Pyrroloquinoline Quinone Disodium Salt (PQQ): Benefits, Uses, and Safety Guide
Introduction
Pyrroloquinoline Quinone Disodium Salt (PQQ) is a stable, water-soluble form of PQQ, a redox cofactor with potent antioxidant properties. Found naturally in trace amounts in foods like kiwifruit, parsley, and green peppers, PQQ is widely used in dietary supplements for its cellular and neurological benefits. Over 80% of commercial supplements utilize the disodium salt form due to its enhanced stability and bioavailability .
Key Features
- Chemical Formula: C₁₄H₄N₂Na₂O₈ (Molecular Weight: 374.17)
- Appearance: Reddish-brown to red-orange fine powder
- Purity: ≥98% (HPLC verified)
- Solubility: 3 g/L in water at 25°C
- Shelf Life: Stable for 36 months when stored in sealed containers, away from light and moisture .
Health Benefits
- Boosts Cellular Energy: PQQ activates mitochondrial biogenesis, enhancing ATP production and cellular vitality .
- Supports Cognitive Function: Clinical studies show improved memory, cognitive flexibility, and executive speed, particularly in younger adults (20–40 years) .
- Antioxidant & Neuroprotective Effects: Neutralizes free radicals, reduces oxidative stress, and promotes nerve growth factor (NGF) synthesis .
- Cardiovascular Health: Protects against oxidative damage in blood vessels and supports heart function .
- Anti-Aging Potential: Enhances skin health by reducing oxidative damage and improving collagen synthesis .
Applications & Dosage
- Common Forms:Recommended Daily Intake: 10–20 mg for general health; higher doses (up to 40 mg) may be used under medical supervision .
- Capsules/Softgels: 10–20 mg (often combined with CoQ10 for synergistic effects) .
- Powders/Liquids: 7–20 mg per serving, ideal for drink mixes or functional foods .
- Formulation Flexibility:
- PQQ Disodium Salt: Water-soluble, suitable for capsules, tablets, and powdered beverages.
- PQQ Acid: Oil-soluble, ideal for softgels and emulsified beverages .
Quality & Safety
- Third-Party Testing: Verified for purity (≥98%) and low heavy metal content (lead ≤0.5 ppm, arsenic ≤1 ppm) .
- Safety Profile: Generally recognized as safe (GRAS) at recommended doses. Consult a healthcare provider if pregnant, nursing, or taking medications .
- Storage: Store in cool, dry conditions (2–8°C) to maintain stability .
Key Considerations
- Natural Sources vs. Supplements: While PQQ exists in foods, supplementation is necessary to achieve clinically effective doses .
- Regulatory Status: Approved as a novel food ingredient in the EU and China, with ongoing research to expand applications