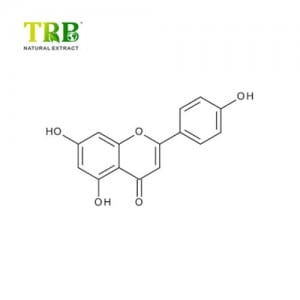
Product Name:Celery leaf extract Apigenin 98%
Latin Name:Apium graveolens L.
CAS No:520-36-5
Plant Part Used:Leaf
Ingredient:Apigenin
Assay:Apigenin 98.0% by HPLC
Colour:Brown to yellow powder with characteristic odor and taste
GMO Status:GMO Free
Packing: in 25kgs fiber drums
Storage:Keep container unopened in cool, dry place,Keep away from strong light
Shelf Life:24 months from date of production
Celery Seed Extract 98% Apigenin: Premium Natural Supplement for Holistic Health
Product Overview
Celery Seed Extract 98% Apigenin is a high-purity natural ingredient derived from the seeds of Apium graveolens, standardized to deliver 98% apigenin—a potent bioactive flavonoid renowned for its multifaceted health benefits. This extract is produced through advanced ethanol-water extraction and quality-controlled processes, ensuring optimal potency and safety. Ideal for nutraceutical, functional food, and pharmaceutical applications, it combines traditional herbal wisdom with modern scientific validation.
Key Health Benefits
- Cardiovascular Support
- Lowers Blood Pressure & Cholesterol: Contains phthalides (e.g., 3-n-butylphthalide) and flavonoids that relax blood vessels, reduce lipid levels (TC, LDL-C, TG), and improve circulation, supporting heart health.
- Anti-Hypertensive Effects: Demonstrated in clinical trials to enhance vasodilation and regulate calcium/potassium flow in vascular cells, reducing hypertension risks.
- Anti-Inflammatory & Antioxidant Properties
- Combats chronic inflammation linked to arthritis, liver disorders, and cardiovascular diseases via flavonoids (apigenin, quercetin) and polysaccharides.
- Neutralizes free radicals with phenolic acids (caffeic acid, ferulic acid), protecting against oxidative stress and cellular damage.
- Hepatoprotective & Digestive Aid
- Reduces liver fat accumulation, improves enzyme function, and promotes detoxification by enhancing bile flow.
- Acts as a diuretic, alleviates bloating, and supports gut health by balancing gastric mucus and reducing ulcer formation.
- Cancer Prevention & Immune Support
- Apigenin inhibits tumor growth by modulating hormone activity, blocking mutagenic cell proliferation, and protecting DNA integrity.
- Polyacetylenes and antimicrobial compounds combat bacterial infections (e.g., UTIs) and strengthen immune defenses.
- Metabolic & Cognitive Enhancement
- Boosts mitochondrial function, aids weight management, and enhances exercise performance by optimizing lipid metabolism.
- Supports neuroprotection and cognitive health through apigenin’s role in stimulating neurogenesis and reducing neuroinflammation.
Applications
- Nutraceuticals: Formulated in capsules (500–1500 mg/day) for heart health, anti-aging, and immune support.
- Functional Foods: Added to beverages, protein bars, and snacks for metabolic and antioxidant benefits.
- Pharmaceuticals: Used in antihypertensive formulations, hepatoprotective drugs, and anti-cancer adjuvants.
- Cosmeceuticals: Incorporated into skincare for anti-inflammatory and collagen-synthesizing effects.
- Flavoring Agent: Enhances savory profiles in soups, sauces, and meat products as a natural alternative to synthetic additives.
Technical Specifications
- Active Ingredient: Apigenin ≥98% (HPLC).
- Extraction Method: Ethanol-water solvent, spray-dried with maltodextrin.
- Appearance: Fine white to off-white powder.
- Certifications: Non-GMO, gluten-free, no additives.
Why Choose Us?
- Customization: Available in bulk powder, capsules, or liquid extracts for private labeling.
- Fast Delivery: Shipped via DHL/FedEx (5–10 days) or sea freight (15–45 days).
- Quality Assurance: Third-party tested for purity, potency, and heavy metals.
- Free Samples: 5–10 g samples provided for lab verification.
Safety & Usage
- Dosage: 500–1500 mg daily, adjusted for specific formulations.
- Precautions: May interact with CYP3A4-metabolized drugs (e.g., statins, anticoagulants). Consult a healthcare provider if pregnant or on medication
Anti-tumor effect
Apigenin plays an essential role in cancer prevention by inducing apoptosis in various cell lines.
Ovarian cancer:
Some research was found that apigenin could inhibit the growth, proliferation, and transfer of ca-ov3 (human ovarian cancer cell); it induces apoptosis of ca-ov3 through keeping the cancer cells stasis in G2/M phase. The effect is related to time and dose.
Pancreatic cancer:
Apigenin can inhibit the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells. Apigenin starves the tumor by reducing the source of glucose, which is the food on which cancers cells live. Besides, Apigenin can improve the effectiveness of the chemotherapy drug- gemcitabine.
Chemo-sensitization
It was found that apigenin in low content had a low cytotoxic effect and could not induce human acute myeloid leukemia (hl-60) cells to apoptosis effectively. However, apigenin can enhance the inhibitory effect of cisplatin (DDP) on hl-60 cell proliferation while combining with different concentrations of DDP. So Apigenin may have chemotherapy-sensitization effect on hl-60; Low concentrations of apigenin can also reduce the resistance of hl-60 cells to chemotherapy-induced apoptosis, which may be related to the down-regulation of NF-κB and BCL-2. (NF-KB is a kind of protein complex that controls DNA transcription, the production of cytokines and cell survival; BCL-2 is encoded in the body through the BCL2 gene, it is the original member of the BCL-2 regulatory proteins family that can regulate cell death )
Liver protection
Apigenin can reduce liver injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion through antagonizing lipid peroxidation and scavenging free radicals.
Apigenin can reduce liver injury caused by oxidative stress due to its potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities.
Pharmacological experiments have proved that apigenin has an apparent protective effect on alcohol-induced liver/hepatocyte injury, and its primary mechanism is related to the inhibition of CYP2E1 expression in the liver/hepatocyte.
Prevent osteoporosis
Apigenin inhibits osteoblastogenesis, osteoclastogenesis, and also prevents bone loss.
Apigenin protects bone tissue by reducing bone loss in the body.
Some studies related to the MC3T3-E1, an osteoblast precursor cell line derived from Mus musculus (mouse) calvaria, found that apigenin can inhibit the TNF-α, IFN-γ, and then induced the secretion of several cytokines that promote osteoclast formation.
Apigenin also inhibited the differentiation of 3T3-L1 adipose precursor cells into adipocytes strongly, therefore inhibiting the differentiation attendant inhibition adipocyte differentiation-induced IL-6, MCP-1, lectin product.
Apigenin inhibits the differentiation of osteoclasts from RAW264.7 cell lines and then inhibits the formation of multinucleated osteoclasts. It can also induce osteoclast apoptosis and inhibit bone resorption.
Anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant activity
Apigenin restrains the inflammation process, increases the IL-10 levels and normalizes the oxidative stress parameters
Apigenin inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines and induces the anti-inflammatory cytokine production.
Some literature suggests that apigenin alleviates tissue inflammation induced by oxidative stress in tissues by modulating various oxidative stress markers, interleukins, blood enzyme markers, and expression of several other related enzymes.
Regulation of endocrine
Apigenin can regulate blood sugar, treat thyroid insufficiency and control lipid peroxidation.It was found that apigenin could increase the levels of insulin and thyroxine in diabetic animals, and decrease the concentration of blood sugar and the activity of glucose-6-phosphorylase (G-6-Pase).
Apigenin reversed the effects of increased serum cholesterol, increased liver lipid peroxidation (LPO) and decreased activities of antioxidants such as catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) in alloxan-induced animals.
In animals with regular blood sugar, apigenin can also reduce serum cholesterol and liver lipid peroxidation, and increase the activity of antioxidants in cells.
Pharmacological properties of apigenin
Apigenin has been attached great importance in recent years, as a beneficial health promoter on account of its lower intrinsic toxicity and its health effects on regular versus cancer cells, compared with other structurally related flavonoids. There is a bulk of research evidence that has shown apigenin has great therapeutic potential for many diseases